TL;DR
We are going to talk about how does JavaScript method get called from native. Contents in this chapter can be covered by below figure.
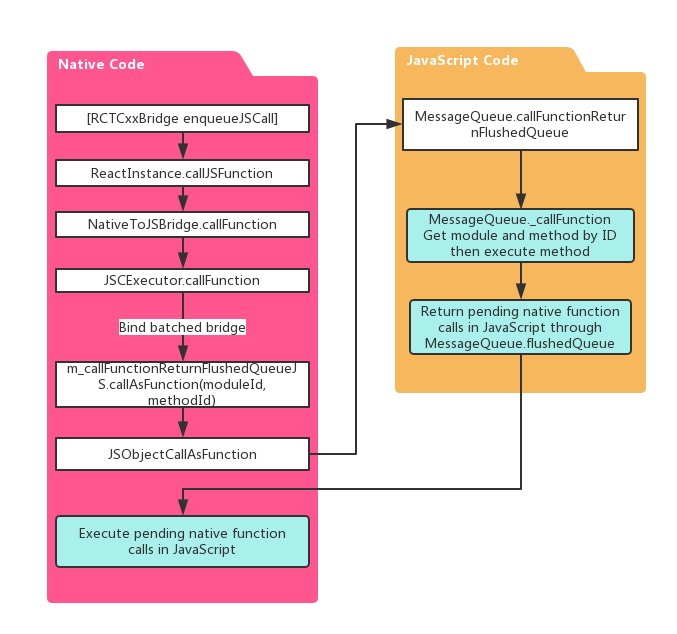
At the end of this chapter there is an experiment about how to export JavaScript methods and call it from native.
Since you want to read it anyway...
As we mentioned in last chapter, When RCTBridge is done with initialization it will notify RCTRootView to call AppRegistry.runApplication to run our JavaScript code. This chapter will focus on how does JavaScript method get called from native code.
RCTRootView.m
- (void)runApplication:(RCTBridge *)bridge
{
//...
[bridge enqueueJSCall:@"AppRegistry"
method:@"runApplication"
args:@[moduleName, appParameters]
completion:NULL];
}
RCTCxxBridge.mm
- (void)enqueueJSCall:(NSString *)module method:(NSString *)method args:(NSArray *)args completion:(dispatch_block_t)completion
{
//...
[self _runAfterLoad:^(){
//...
if (strongSelf->_reactInstance) {
strongSelf->_reactInstance->callJSFunction([module UTF8String], [method UTF8String],
convertIdToFollyDynamic(args ?: @[]));
//...Completion code
}
}];
}
Instance.cpp
void Instance::callJSFunction(std::string &&module, std::string &&method,
folly::dynamic &¶ms) {
//...
nativeToJsBridge_->callFunction(std::move(module), std::move(method),
std::move(params));
}
NativeToJsBridge.cpp
void NativeToJsBridge::callFunction(
std::string&& module,
std::string&& method,
folly::dynamic&& arguments) {
//...
runOnExecutorQueue([module = std::move(module), method = std::move(method), arguments = std::move(arguments), systraceCookie]
(JSExecutor* executor) {
//...
executor->callFunction(module, method, arguments);
});
}
After three bridged call, the JSCExecutor finally join the party.
JSCExecutor.cpp
void JSCExecutor::callFunction(const std::string& moduleId,
const std::string& methodId,
const folly::dynamic& arguments) {
//...
// This weird pattern is because Value is not default constructible.
// The lambda is inlined, so there's no overhead.
auto result = [&] {
JSContextLock lock(m_context);
try {
if (!m_callFunctionReturnResultAndFlushedQueueJS) {
bindBridge();
}
/**
* Bob's note:
* This is where js functions get called.
*/
return m_callFunctionReturnFlushedQueueJS->callAsFunction({
Value(m_context, String::createExpectingAscii(m_context, moduleId)),
Value(m_context, String::createExpectingAscii(m_context, methodId)),
Value::fromDynamic(m_context, std::move(arguments))
});
} catch (...) {
//...Throw error
}
}();
/**
* Bob's note:
* Get pending native calls from JavaScript when done with JavaScript function call.
**/
callNativeModules(std::move(result));
}
/**
* Bob's note:
* Get objects (or functions) in JSContext defined by JavaScript.
**/
void JSCExecutor::bindBridge() throw(JSException) {
//...
std::call_once(m_bindFlag, [this] {
auto global = Object::getGlobalObject(m_context);
auto batchedBridgeValue = global.getProperty("__fbBatchedBridge");
if (batchedBridgeValue.isUndefined()) {
auto requireBatchedBridge = global.getProperty("__fbRequireBatchedBridge");
if (!requireBatchedBridge.isUndefined()) {
batchedBridgeValue = requireBatchedBridge.asObject().callAsFunction({});
}
if (batchedBridgeValue.isUndefined()) {
throw JSException("Could not get BatchedBridge, make sure your bundle is packaged correctly");
}
}
auto batchedBridge = batchedBridgeValue.asObject();
m_callFunctionReturnFlushedQueueJS = batchedBridge.getProperty("callFunctionReturnFlushedQueue").asObject();
m_invokeCallbackAndReturnFlushedQueueJS = batchedBridge.getProperty("invokeCallbackAndReturnFlushedQueue").asObject();
m_flushedQueueJS = batchedBridge.getProperty("flushedQueue").asObject();
m_callFunctionReturnResultAndFlushedQueueJS = batchedBridge.getProperty("callFunctionReturnResultAndFlushedQueue").asObject();
});
}
This is the key part of how native code calling JavaScript functions. All JavaScript calls from native will dispatched by a 'BatchedBridge', which is a object defined in 'JSContext' using JavaScript. This 'BatchedBridge' contains several functions which will dispatch JavaScript methods for native code. When calling callFunction, JavaScript executor will first check whether BatchedBridge is bound with itself or not. Then it will dispatch JavaScript call using m_callFunctionReturnFlushedQueueJS. This is a function exported in JavaScript code and we retrieved it from 'JSContext' in bindBridge function.
Also you may find out functions like asObject , getProperty and callAsFunction are very convenient but doesn't look familiar. This is a C++ wrapper for JSObjectRef and JSValueRef which defined in ReactCommon/jschelpers/Value.h. This wrapper also bridging function calls between itself and JavaScriptCore . For example callAsFunction is implemented like this:
Value.m
Value Object::callAsFunction(JSObjectRef thisObj, int nArgs, const JSValueRef args[]) const {
JSValueRef exn;
JSValueRef result = JSC_JSObjectCallAsFunction(m_context, m_obj, thisObj, nArgs, args, &exn);
if (!result) {
throw JSException(m_context, exn, "Exception calling object as function");
}
return Value(m_context, result);
}
JavaScriptCore.h
#define JSC_JSObjectCallAsFunction(...) __jsc_wrapper(JSObjectCallAsFunction, __VA_ARGS__)
So the underlying function of JSValue::callAsFunction is JSObjectCallAsFuntion provided by Apple's JavaScriptCore. You can read more about this function in Apple's documents. But as you can guess from the function name, it will call an object as function.
Before we getting any further with 'BatchedBridge', there is another important part: How does native methods get called in JavaScript. We will not dig into it in this chapter but long story short - calls are not made in real time. There is a 'queue' for all native calls from JavaScript. And when we are done with JavaScript calls, the queue will be passed to native and all items in it will be executed. That's why those functions have '***ReturnFlushedQueueJS' names.
Now let's find out what's happening in ReactNative's 'BatchedBridge'.
BatchedBridge.js
const BatchedBridge = new MessageQueue(
// $FlowFixMe
typeof __fbUninstallRNGlobalErrorHandler !== 'undefined' &&
__fbUninstallRNGlobalErrorHandler === true, // eslint-disable-line no-undef
);
// Wire up the batched bridge on the global object so that we can call into it.
// Ideally, this would be the inverse relationship. I.e. the native environment
// provides this global directly with its script embedded. Then this module
// would export it. A possible fix would be to trim the dependencies in
// MessageQueue to its minimal features and embed that in the native runtime.
Object.defineProperty(global, '__fbBatchedBridge', {
configurable: true,
value: BatchedBridge,
});
module.exports = BatchedBridge;
The MessageQueue module is injected to JSContext in this file and worked as 'BatchedQueue'.
MessageQueue.js
callFunctionReturnFlushedQueue(module: string, method: string, args: any[]) {
this.__guard(() => {
this.__callFunction(module, method, args);
});
return this.flushedQueue();
}
__callFunction(module: string, method: string, args: any[]): any {
this._lastFlush = new Date().getTime();
this._eventLoopStartTime = this._lastFlush;
//...
const moduleMethods = this.getCallableModule(module);
//...Assert module and method exist.
const result = moduleMethods[method].apply(moduleMethods, args);
return result;
}
getCallableModule(name: string) {
const getValue = this._lazyCallableModules[name];
return getValue ? getValue() : null;
}
This is quite simple too: find the module and method, then execute it.
So the question is - where does those module and methods come from? Does all methods in JavaScript can be called in native?
Answer is no. In order to export your JavaScript method to native, you must register it to _lazyCallableModules in 'MessageQueue'.
MessageQueue.js
registerCallableModule(name: string, module: Object) {
this._lazyCallableModules[name] = () => module;
}
For example you can find code about how AppRegistry registered itself:
AppRegistry.js
BatchedBridge.registerCallableModule('AppRegistry', AppRegistry);
That's basically explained how native code calling JavaScript methods. In next chapter we will start talk about how native methods get called from JavaScript.
Get your hands dirty.
Here is a little experiment about how to export your own JavaScript method to native code.
First define your JavaScript method in 'App.js' and register it in BatchedBridge.
App.js
//...imports
const BatchedBridge = require('BatchedBridge');
const JSLog = { log: (msg) => { console.log(msg); }};
export default class App extends Component<{}> {
constructor(props) {
super(props);
BatchedBridge.registerCallableModule("JSLog", JSLog);
}
//...
}
Then modify native code to add a button which will trigger this function.
AppDelegate.m
@interface AppDelegate()
@property(strong, nonatomic) RCTRootView* rootView;
@end
@implementation AppDelegate
- (BOOL)application:(UIApplication *)application didFinishLaunchingWithOptions:(NSDictionary *)launchOptions
{
//...jsCodeLocation
_rootView = //...Create RCTRootView
//...Add an UIButton natively to trigger js call
UIButton *button = [[UIButton alloc] initWithFrame:CGRectMake(20, 20, 100, 100)];
button.backgroundColor = UIColor.cyanColor;
[button setTitle:@"Call log in js" forState:UIControlStateNormal];
[button addTarget:self action:@selector(callLogInJS) forControlEvents:UIControlEventTouchUpInside];
self.window = [[UIWindow alloc] initWithFrame:[UIScreen mainScreen].bounds];
UIViewController *rootViewController = [UIViewController new];
[_rootView addSubview:button];
rootViewController.view = _rootView;
//...Set window's root view controller
}
- (void)callLogInJS {
[_rootView.bridge enqueueJSCall:@"JSLog.log" args:@[@"------stab!-------"]];
}
@end
That's all. When you press the button in root viewcontroller, it will call our log function through BatchedBridge.